Innovative Cooling Mechanism That Requires no Electricity
A cooling method that makes use of sunlight and salt to run, paving way for future self-sustainable technologies
In this day and age electricity has become an integral part of our life. Air conditioners are not less than a bliss during summers but without electric power, this innovation would have not been of any use.
There are around 940 million people in the world including some extremely hot countries like Niger and Mali who do not have access to electricity, which means neither they use air conditioners nor do they have technological advancement for using solar energy in their daily life. As a ray of hope a new technology can help people living in such regions to cool down, and that too without the need for an electric power source.
This innovation is nothing but a basic chemical reaction, which was first developed at Saudi Arabia’s King Abdullah University of Science and Technology. For now, the method is in its early stages but it will definitely serve as a great solution to the problem.
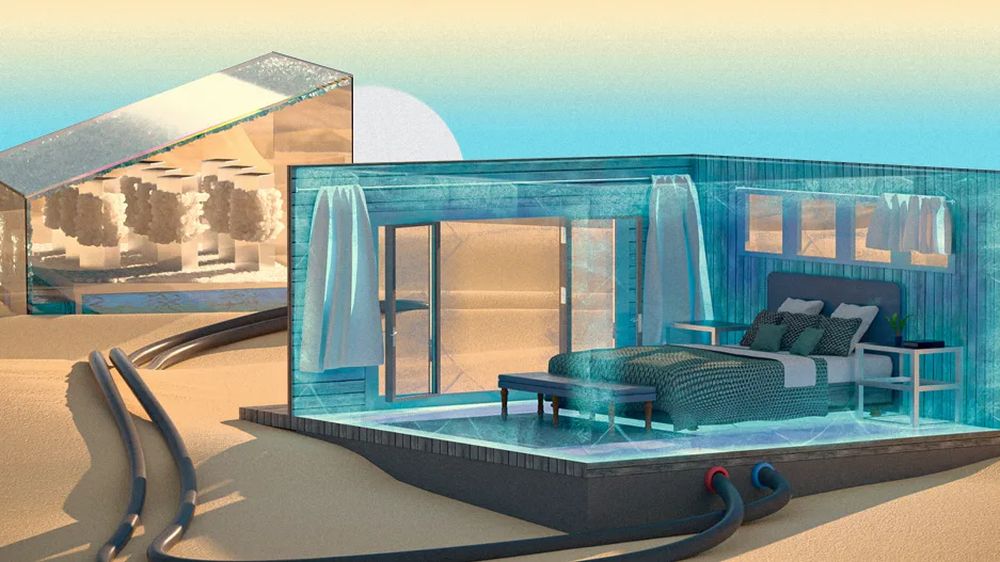
Image: King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
Some salts are liquefied in water and these salts absorb heat that eventually cools down the water temperature. If the process is on a larger scale it could provide a great cooling effect without using electricity.
Dr. Peng Wang, an environmental science and engineering professor at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology who is leading the research mentions;
In underdeveloped regions, this can help them store food for a couple more days.
In one of the lab tests led by the team at the University of Science and Technology, it was found that the temperature remained below 50°F for eight hours and under 59°F for over 15 hours, which would be sufficient to store food for one day.
The researchers aim at building a demonstration unit, according to Mr. Wang it can be as big as the size of a fridge or as small as a lunchbox. Alongside it can also serve as a cooling mattress. The unit could regenerate itself if kept on the roof in the backyard.
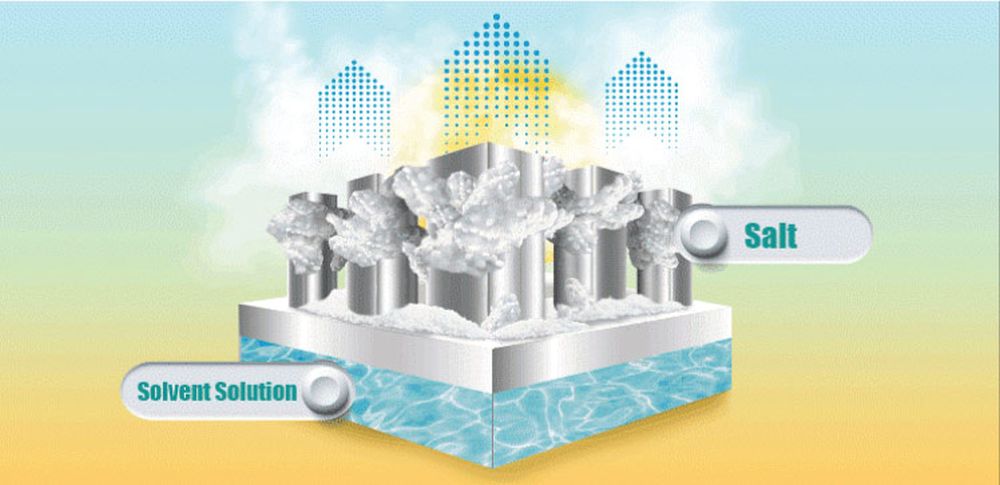
Image: King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
The process takes one hour to restore the salt in two liters of water halting its efficiency. Addressing the problem Dr. Wang explains that solar energy can be stored for later use which means cooling would be offered when required.
You can use today’s solar energy to provide cooling power in a week
He says.
Ammonium nitrate’s salt is used as it is highly dissolvable in water and is easily available. Providing water for this technology would be a great challenge especially in arid regions. So the team of researchers is now working on ways to recover the water in sustainable ways.
The technology does not really offer a lot at this point in time but it can be a useful device in the future for people who do not have access to basic facilities like electricity.
Via: Fast Company


